purposive sampling in quantitative research|purposive sampling in research example : discount store Purposive sampling is a non-probability sampling technique used in research to select individuals or groups of individuals that meet specific criteria relevant to the . web16 de mar. de 2022 · Login here to access the FC Ultimate Team App and manage your Ultimate Team while you're away from your console or PC.
{plog:ftitle_list}
Resultado da 3 dias atrás · Intel® Core™ i3-2100 Processor (3M Cache, 3.10 GHz) quick reference with specifications, features, and technologies.
Purposive sampling is a non-probability method that relies on researcher's judgment to choose cases that help answer research questions. It can be used i. Purposive sampling is a non-probability sampling technique used in research to select individuals or groups of individuals that meet specific criteria relevant to the . Making explicit the approach used for participant sampling provides improved methodological rigour as judged by the four aspects of trustworthiness. The cases presented provide a guide for novice researchers .Purposive sampling is a qualitative and mixed methods technique of selecting informants based on their ability to elucidate a specific theme, concept, or phenomenon. It involves .
Purposive sampling is a non-probability method for obtaining a sample where researchers use their expertise to choose specific participants that will help the study meet its goals. Learn about the types of purposive sampling, such . Purposive Sampling. Sometimes selecting respondents based on convenience defeats the purpose of a study. In some cases, a researcher needs to target very specific .
Purposive sampling, also known as judgmental or expert sampling, involves intentional selection of participants based on the researcher’s expertise. Participants are chosen deliberately, not randomly, to align with .The sampling strategies clearly situate each study in terms of trustworthiness for data collection and analysis. The selected approach to purposive sampling used in each case aligns to the .
what is purposive sampling in qualitative research
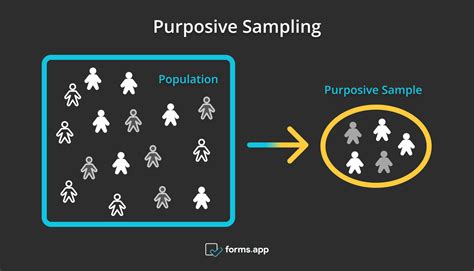
Purposive sampling allows for the essential task of generating new knowledge through the processes of comparison and contrast. As one cannot assume knowledge of the . Purposive sampling is a technique used in qualitative research to select a specific group of individuals or units for analysis. Participants are chosen “on purpose,” not randomly. It is also known as judgmental sampling or selective sampling. In purposive sampling, the researcher has a specific purpose or objective in mind when selecting the sample.Purposive sampling. Purposive sampling, also known as judgmental, selective or subjective sampling, is a type of non-probability sampling technique.Non-probability sampling focuses on sampling techniques where the units that are investigated are based on the judgement of the researcher [see our articles: Non-probability sampling to learn more about non-probability .
This research uses interview and focus group discussion (FGD) study methods to obtain various information. Purposive sampling was used to determine the research area (Nyimbili and Nyimbili, 2024 .
The purposive sampling technique is a type of non-probability sampling that is most effective when one needs to study a certain cultural domain with knowledgeable experts within. Purposive sampling may also be used with both qualitative and quantitative research techniques. The inherent bias of the method contributes to its efficiency, and the .Background: Purposive sampling has a long developmental history and there are as many views that it is simple and straightforward as there are about its complexity. The reason for purposive sampling is the better matching of the sample to the aims and objectives of the research, thus improving the rigour of the study and trustworthiness of the data and results.Quantitative researchers tend to use a type of . Purposive sampling is an acceptable kind of sampling for special situations. It uses the judgment of an expert . (RDD) is a special sampling technique used in research projects in which the general public is interviewed by telephone. Here is how RDD works in the United States. Telephone . What is Purposive Sampling? Methods, Techniques, and Examples
Further, the numerous technique options outlined above make purposive sampling a versatile research method that can be tailored to enhance a survey’s effectiveness. Sometimes purposive sampling may be the only appropriate method available if there are a limited number of primary data sources that can contribute to the survey. Drawbacks of . Purposive sampling may also be used with both qualitative and quantitative research techniques. The inherent bias of the method contributes to its efficiency, and the method stays robust even when . As utilized in qualitative and mixed methods research, purposive sampling involves an iterative process of selecting research subjects rather than starting with a predetermined sampling frame.Akin to grounded theory, the selection process involves identifying themes, concepts, and indicators through observation and reflection (Schutt 2006: .
There are two primary types of sampling methods that you can use in your research: Probability sampling involves random selection, . It is mainly used in quantitative research. If you want to produce results that are representative of the whole population, probability sampling techniques are the most valid choice. . Purposive sampling You . Expert sampling is a form of purposive sampling used when research requires one to capture knowledge rooted in a particular form of expertise. It is common to use this form of purposive sampling technique in the early stages of a research process, when the researcher is seeking to become better informed about the topic at hand before embarking . Expert purposive sampling is used when the researcher needs to obtain knowledge from individuals with particular expertise. This skill may be necessary during the starting phase of qualitative research design because it can help understand new areas of interest. Purposive Sampling Example. Purposive sampling can be used in educational .
Purposive sampling is a data collection technique with consideration of certain criteria to achieve research objectives (Campbell et al., 2020). 2 media experts were determined based on purposive .
SAMPLING. Sampling can be defined as the process through which individuals or sampling units are selected from the sample frame. The sampling strategy needs to be specified in advance, given that the sampling method may affect the sample size estimation. 1,5 Without a rigorous sampling plan the estimates derived from the study may be biased (selection bias). 3
So here, we have an example of critical case purposive sampling, where a country or a particular city is selected for better and more accurate research. Since religion is a sensitive topic, this type of sampling is . When using purposive sampling, the researcher has the freedom to choose a sample size he/she/they think have the best suitable characteristics to give him/her/them an in-depth and quality . Non-probability sampling in quantitative research was also delineated as a way to maximise response rate. . purposive sample owing to its reliance on the use of a purposive sampling process i.e .
Non-probability sampling methods are those in which elements are chosen through non-random methods for inclusion into the research study and include convenience sampling, purposive sampling, and . Any senior researcher, or seasoned mentor, has a practiced response to the ‘how many’ question. Mine tends to start with a reminder about the different philosophical assumptions undergirding qualitative and quantitative research projects (Staller, 2013).As Abrams (2010) points out, this difference leads to “major differences in sampling goals and strategies.”(p.537).
what does purposive sampling mean
Purposive sampling procedures are used in most research papers because they are found in . quantitative research, the larger the sample the better, as this not only gives greater reliability
Adopting purposive sampling for your research helps you to extract lots of information from research participants, especially when there are just a few of them. On the flip side, it can ruin your data collection process if you make subjective or generalized assumptions when selecting variables for your data collection process.Introduction. In qualitative research studies that involve methods such as interviews, focus groups, and surveys, purposive sampling is useful when the researcher wants to collect qualitative data from a specific population with particular characteristics.. Purposive sampling or judgmental sampling stands in contrast to random sampling or probability sampling, which . This chapter explains how to design suitable sampling strategies for qualitative research. The focus of this chapter is purposive (or theoretical) sampling to produce credible and trustworthy explanations of a phenomenon (a specific aspect of society). A specific research question (RQ) guides the methodology (the study design or approach).It defines the .
Probability-based sampling methods are most commonly used in quantitative research, especially when it’s important to achieve a representative sample that allows the researcher to generalise their findings. Non-probability sampling, on the other hand, refers to sampling methods in which the selection of participants is not statistically random. Purposeful sampling is a technique widely used in qualitative research for the identification and selection of information-rich cases for the most effective use of limited resources (Patton 2002).This involves identifying and selecting individuals or groups of individuals that are especially knowledgeable about or experienced with a phenomenon of interest (Cresswell and .
This article will outline the guiding principles and rationales, features, and practices of sampling in qualitative research. It then describes common questions about sampling in qualitative research.

scratch test for liver
purposive sampling technique qualitative
web24 de out. de 2023 · 対戦回避ペナルティの段階は、12時間ごとに1段階ずつ自動的に低下していきます。 昇格戦シリーズで対戦を回避すると、その対戦は敗北とみなされます。 シリーズの決勝戦を回避した場合、その対戦は敗北とみなされ、シリーズは終了となります。
purposive sampling in quantitative research|purposive sampling in research example